Estimating Appliance and Home Electronic Energy Use refers to the process of assessing and approximating the energy consumption of various household appliances and electronic devices. This estimation is crucial for understanding and managing energy usage within a home, aiming to promote efficiency and reduce overall energy costs.
The procedure typically involves identifying and analyzing the energy consumption patterns of individual appliances and electronics. This may include factors such as the wattage of each device, the duration of usage, and the frequency of operation. By gathering this information, homeowners can make informed decisions about energy-efficient practices, potentially leading to lower utility bills and a reduced environmental impact.
Estimating appliance and electronic energy use may also involve the use of energy monitoring tools or smart devices that provide real-time data on energy consumption. These tools offer insights into which appliances consume the most energy, allowing users to adjust their usage habits or consider more energy-efficient alternatives.
Ultimately, the goal of estimating appliance and home electronic energy use is to empower individuals to make conscious choices that align with energy conservation efforts, contributing to both cost savings and environmental sustainability.
Methods to gauge the electricity consumption
There are various methods to gauge the electricity consumption of your appliances and home electronics:
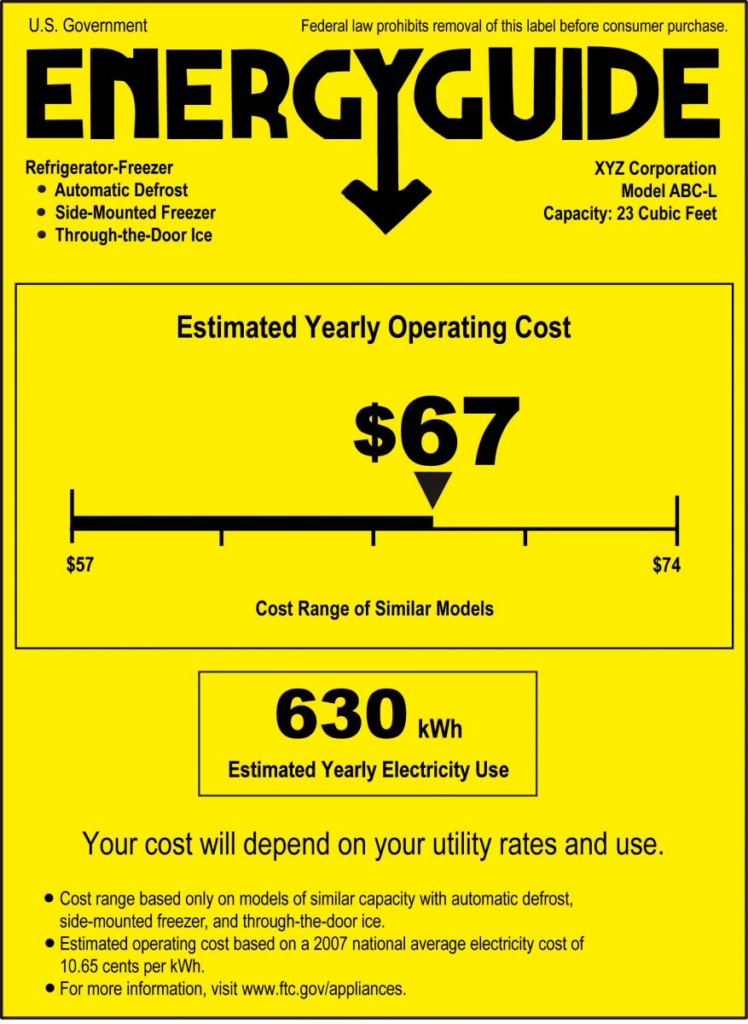
- Examining the Energy Guide label: This label offers an approximation of the average energy consumption and operating costs associated with the particular model of the appliance in use. It’s important to note that not all appliances or home electronics are mandated to feature an Energy Guide.
- Employing an electricity usage monitor: This device provides readings to determine the electricity consumption of an appliance.
- Computing annual energy consumption and costs using the provided formulas.
- Implementing a comprehensive home energy monitoring system.
- Electricity Usage Monitors
To determine the wattage of a device, simply insert the monitor into the electrical outlet the device is connected to and then plug the device into the monitor. The monitor will display the device’s wattage. For those interested in calculating the kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity consumed by the device over a specified period, leave the setup as is and check the display later.
These monitors are particularly helpful in assessing the kWh usage over time for devices that do not run continuously, such as refrigerators. Some monitors allow users to input their utility’s per-kilowatt-hour charge, providing an estimate of the cost to operate the device since it was connected to the monitor.
Additionally, many appliances continue to draw a small standby power when turned “off,” referred to as “phantom loads.” These loads are present in most electricity-consuming appliances, including televisions, stereos, computers, and kitchen appliances. A monitor can be used to estimate these phantom loads, typically adding a few watt-hours to the appliance’s energy consumption. To avoid these loads, one can unplug the appliance or use a power strip with a switch to cut all power to the appliance.
Calculating Annual Electricity Consumption and Costs
Calculating the yearly electricity consumption and associated costs can be achieved by following these steps:
1. Estimate the daily operating hours of the appliance. This can be done in two ways:
- Rough estimate: If you have a general idea of how frequently you use the appliance daily, use that information. For instance, if you typically watch television for about 4 hours daily or run a whole-house fan for 4 hours each night, these estimates can be applied. To gauge the actual operating hours of a refrigerator at its maximum wattage, divide the total time the refrigerator is plugged in by three. Despite being “on” continuously, refrigerators cycle on and off to maintain interior temperatures.
- Keep a log: Maintain a usage log for certain appliances. Record the cooking time for the microwave, computer usage duration, television watching time, or the duration lights are left on in a room or outdoors.
2. Determine the wattage of the product, which can be done in three ways:
- Stamped on the appliance: Most appliances have their wattage stamped on the bottom, back, or nameplate. This value represents the maximum power the appliance draws. As many appliances have variable settings, the actual power consumption depends on the selected setting. For example, a radio at high volume consumes more power than one at low volume, and a fan at a higher speed uses more power than at a lower speed.
- Multiply the appliance ampere usage by the appliance voltage usage: If the wattage is not visibly stated on the appliance, estimate it by determining the electrical current draw (in amperes) and multiplying it by the appliance’s voltage usage. In the United States, most appliances use 120 volts, while larger ones, like clothes dryers and electric cooktops, use 240 volts. The amperes may be indicated on the unit or listed in the owner’s manual or specification sheet.
- Use online sources to find typical wattages or the wattage of specific products you are considering purchasing. The following links are good options:
The Home Energy Saver provides a list of appliances with their estimated wattage and their annual energy use, along with other characteristics (including annual energy use, based on “typical” usage patterns. Continue using the equations here if you want to find energy use based on your own usage patterns).
ENERGY STAR offers energy-use information on specific products that have earned the ENERGY STAR. The information varies across products, but if you are considering purchasing a new, efficient product, ENERGY STAR allows you to select and compare specific models. In some cases, you can use the provided information to do your own estimates using the equations here. The information may also help you compare your current appliances with more efficient models, so you understand potential savings from upgrading to a more efficient appliance.
Find the daily energy consumption using the following formula:
(Wattage × Hours Used Per Day) ÷ 1000 = Daily Kilowatt-hour (kWh) consumption
Find the annual energy consumption using the following formula:
Daily kWh consumption × number of days used per year = annual energy consumption
Find the annual cost to run the appliance using the following formula:
Annual energy consumption × utility rate per kWh = annual cost to run appliance
Examples:
I. Following the aforementioned procedure, determine the yearly operational cost of an electric kettle.
1. Estimation of usage time: The kettle is utilized multiple times per day, totaling about 1 hour.
2. Wattage: The wattage, indicated on the label, is specified as 1500 W.
3. Daily energy consumption:
(1,500 W × 1) ÷ 1,000 = 1.5 kWh
4. Annual energy consumption: The kettle is in use nearly every day of the year.
1.5 kWh × 365 = 547.5 kWh
5. Annual cost: The utility rate stands at 11 cents per kWh.
547.5 kWh × $0.11/kWh = $60.23/year
II. Applying the outlined steps, calculate the yearly operational cost of a paper shredder.
1. Estimation of usage time: The shredder is operated for approximately 15 minutes per day (0.25 hours).
2. Wattage: Although not explicitly listed on the label, the electrical current draw is stated as 3 amperes.
120V × 3A = 360W
3. Daily energy consumption:
360 W × .25 ÷ 1000 = 0.09 kWh
4. Annual energy consumption: The shredder is utilized about once per week (52 days per year).
0.09 kWh × 52 = 4.68 kWh
5. Annual cost to operate: The utility rate is 11 cents per kWh.
4.68 kWh × $0.11/kWh = $0.51/year
In conclusion, estimating the annual energy consumption and operational costs of electrical appliances provides valuable insights for energy-conscious consumers. By following simple steps, such as estimating daily usage time and determining power consumption, it is possible to calculate the financial and environmental impact of these devices. These assessments empower consumers to make informed decisions about energy-efficient usage in their homes, fostering awareness of the significance of adopting sustainable practices. Not only does this contribute to personal savings, but it also plays a crucial role in environmental preservation. Understanding the annual operational cost of specific appliances equips consumers to make choices that promote energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
As a company dedicated to energy efficiency, we offer complimentary home energy audits to enhance your home’s energy efficiency. This initiative allows you to cut costs and conserve resources while actively participating in environmental preservation. If you reside in the state of New York, it’s important to note that the government extends various incentives, tax rebates, discounts, and financing options through programs like Clean Heat, Comfort Home, and GJGNY Financing. We are here to support you in navigating these opportunities, verifying your eligibility, and guiding you through the application process. Taking these proactive steps collectively contributes to the creation of a more sustainable and economical future.



